- Home
- Shop
-
Engine & Drivetrain
- Radiators, Fans, Cooling Systems & Components
- Exhaust, Headers, Manifolds Mufflers & Components
- Fuel Systems & Components
- Heating, Air Conditioning & Components
- Air Filters, Oil Filters & Intake Systems
- Electronic Control Modules, Ignition & Distributors
- Cranks, Pistons, Oil & Components
- Cams, Timing & Valvetrain
- Clutches, Flywheels & Components
- Switches, Relays, Wiring & Components
- Oxygen Sensors & Components
- Engine & Transmission Assemblies
- Other Engine Parts
-
Brakes, Suspension & Steering
- Brake Discs, Pads & Calipers
- Shocks, Struts & Components
- Control Arms, Thrust Arms & Components
- Wheel Hubs, Bearings, and Components
- Tie Rods, Steering Racks & Components
- Axles, Axles Carrier, Driveshaft & 4WD
- Power Steering Pumps & Components
- Air Suspension Components
- Other Brakes, Suspension & Steering Parts
- ABS Pump & Components
-
Engine & Drivetrain
- Blog
- Catalog
- Contacts US
- Compare: 0
Product
Categories
Select a vehicle to find exact fit parts
Torque converter: how it works, symptoms of failure, and cost of replacement
If you're the type of person who has a great passion for cars, you have most likely heard, or taken part in, discussions about torque converters. Here you’ll find more information about how it works and what to look out for if you think it’s malfunctioning.
How does a torque converter work?
A modern torque converter works as a transformer to help your car to start and as a clutch to separate or connect the engine and transmission. It is often considered to be the most complicated part of contemporary vehicles. However, it is an essential component of automatic transmissions. The first part of the torque converter is the impeller which has bent blades and contains fluid. When the impeller rotates, this fluid will be directed outwards through the forces generated through the rotation of the impeller. The faster the impeller rotates, the higher the centrifugal forces. The turbine is located opposite the impeller. The fluid flow from the impeller is directed over the blades of the turbine, causing the turbine to rotate. The turbine’s blades are installed in such a way that allows the fluid to flow to the inner part of the turbine and into the impeller. From there the cycle is repeated. The fluid flows through the turbine to the stator. The stator’s curved blades turn the fluid flow at an angle of almost 90 degrees resulting in a multiplication of torque because the fluid flows back more slowly. The impeller is mounted to the housing and the housing is connected to the engine causing the impeller to receive the mechanical energy produced by the engine. In general, torque converters use a lock-up clutch and a turbine output shaft that connects the turbine to the transmission and the wheels of the vehicle.
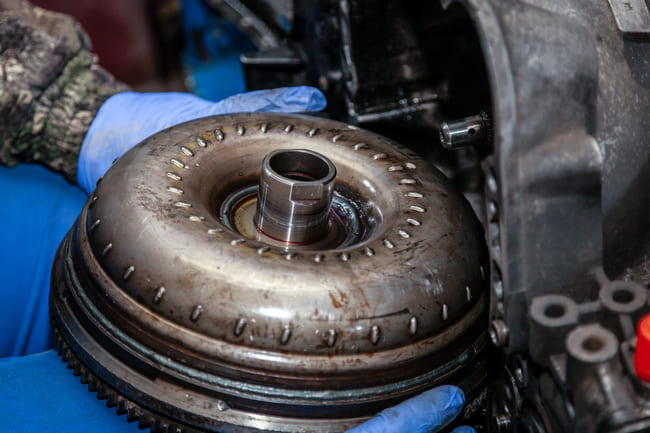
Malfunctioning torque converter symptoms
The most common sign that these components have stopped working properly is a slipping gearbox. You may feel this when the engine speed increases but the car does not accelerate. This symptom is similar to clutch slippage in the manual gearbox – the speedometer needle goes up but the car stops or accelerates much slower. If the torque converter slips while driving, one of the consequences of this problem is the unnecessary heating of the transmission oil and it may eventually boil. In short, if the torque converter is defective and slippery, the car's transmission system will wear out within a very short time. If you experience irregular idling you must consider the fact that the torque converter may not be working properly. Whether the idle is sometimes too low or sometimes too high, something is wrong and the problem may lie with the defective torque converter. Acceleration problems can also be a symptom caused by pressure differences in the converter as well as your car not moving forward or backward at all. It is also important to “keep an ear out” for strange noises coming from the converter. If you begin to hear it making odd sounds, it’s time to get it checked to see if it needs replacing.
Worn bearings are a fairly common problem for defective torque converters. In most cases, this problem does not cause slipping or other problems with the gearbox, but noises can be heard from the car's gearbox due to worn bearings. If you are confronted with such a situation, it is advisable to first check the gear oil and see if the pieces of metal are in the container where the gear oil is. If small pieces of metal are found, 99.99% of them come from one of the bearings of the torque converter. The most important thing to do in case of gearbox problems is to check and replace the gearbox oil. If you check the gearbox oil and find that it is either brown or almost black, it is advisable to replace both the gearbox oil and the gearbox filter, if the car has one. It is better to replacein time, which is not expensive at all while replacing the torque converter would cause a small hole in your budget. Also, when checking the gearbox oil, it is essential to make sure that there are no small pieces of metal that come from used bearings located inside the torque converter.

Malfunctioning clutch magnet
The clutch solenoid is also an important component when it comes to automatic transmission failure. The role of the electromagnet is to control the pressure of the hydraulic pressure fluid entering the lock-up clutch and for this reason, various problems can occur, such as heavy acceleration, slippage, or overheating. If you find that the car is sticking or more specifically the gearbox is locking up when the engine is running in all gears, then it is definitely time to take a look at the torque converter clutch and you should also check the solenoid valve on it. This can be done by disassembling the torque converter and to buy car engine parts to take care of the problem yourself.
Replacing the torque converter
Depending on the problem and the make and model of the car, there are situations where it is more appropriate to replace the entire system than certain sub-components, especially since are not very expensive. This way, time is no longer wasted replacing some of the torque converter's subcomponents. If you intend to buy such a part for your car, it is advisable to know that you should not look for a used torque converter. The reason why such a used part is not recommended, even though it may have a very attractive price, is as simple as possible, namely that the degree of wear of the converter and its ageing is not usually known. Moreover, it is not the most pleasant work to replace the torque converter. So, in order not to spend money on two such components and not to work twice on disassembling and assembling the torque converter, we recommend you to focus on purchasing a new one.




1984375259.png)
135111072.png)
1235885726.png)
732991495.png)
148086775.png)
There are no comments